Get Super Powered with SmartLine
How Remote Monitoring Can Turn Thermal Process Data into Actionable Information
Abhinav Barnwal, Offering Management Lead, Honeywell Thermal Solutions Dale Smith, Global Growth Leader – Connected Services, Honeywell Thermal Solutions
Thermal processing industries need to maximize their productivity sustainably. There is a growing need for facility owners and operators to improve productivity by minimizing unplanned downtime. In today’s competitive business climate, production and process systems must deliver value by operating in the smartest, most efficient and most sustainable manner possible.
Companies that don’t leap to a modern, integrated automation system, risk high energy costs for day-to-day operations, the safety of equipment and personnel; and penalties for failing to meet environmental standards. Isolated, purpose-built solutions for process control also make it difficult to increase production to meet growing customer demand.
Furthermore, the widespread global disruption caused by the coronavirus underscores the importance of being able to monitor and manage installations remotely if personnel are not able to travel to them.
How can the latest integrated technology solutions help optimize thermal processes? How can they help connect production assets securely in the cloud for enhanced control and performance monitoring to make critical asset data available anytime, anywhere? How can a new breed of remote monitoring solutions provide valuable insight into critical thermal processes?
Today’s demands and operating challenges
With rising energy costs, reduced profit margins and increasing demand for quality, manufacturers with thermal processing operations need to increase productivity, eliminate safety risks and reduce operating expenses. Their primary objectives include:
· Increasing plant efficiency to drive ROI and reduce energy costs
· Lowering maintenance costs
· Minimizing unplanned downtime to increase the availability of heating systems
· Reducing emissions to reduce the risk of related taxes and fines
· Enhancing safety
· Boosting productivity to meet customer demand
Additionally, in thermal process systems such as boilers, ovens and furnaces; information that is vital to efficiency, safety and reliability – is often trapped at the equipment level. That’s a problem unless a worker is standing in front of the equipment, and even then, it might be too late. Maintenance technicians are frequently required to travel to thermal processing equipment to troubleshoot and diagnose problems, and don’t always know what tools or parts are required until they’re on site. This can result in multiple return trips to address an issue.
Moreover, the retirement of engineers, operators and technicians familiar with industrial process heating, and the reality of millennials changing jobs frequently, is creating a shortage of proven know-how. There are fewer combustion specialists across the industry and the plant personnel that remain are being given more responsibilities than ever before.
Need for effective controls
When fewer personnel need to do more work, it’s crucial to optimize process control, which means meeting certain parameters over time by using inputs from process and controlling outputs for desired results. Additionally, the provision of remote access capabilities can help safeguard against the long-term disruption caused by global events, such as the coronavirus. Today’s sophisticated technology overcomes these challenges, allowing users to make better decisions related to process, productivity, quality and safety – even if they’re not on site.
Thermal processing personnel must implement real-time controls to measure and control critical process variables, develop methods to remotely monitor these variables, and find ways to predict future behavior of thermal processes. All types of industrial heating operations depend on state-of-the-art automation technology to stay competitive. Those who resist change will be left behind, wondering why their business is declining and being surpassed by competitors. And those who embrace the opportunity that advanced process control and monitoring systems provide will grow and prosper.
Value of a connected solution
Many companies in the thermal processing industry continue to rely on disparate, purpose-built solutions to run critical production processes. They use components from multiple vendors as well as separate platforms and protocols. Complicated wiring schematics and programming sequences are the norm. With multiple vendor systems in place, process steps might include manual data exchange between systems, thereby increasing processing times and the risk of failure. It’s hard to monitor and control a process when it is fragmented across incompatible solutions.
Conversely, the implementation of a single, connected architecture for industrial heating reduces the control “footprint” in most facilities and enables remote monitoring and troubleshooting of crucial production equipment. With control strategies supported by a single integrated solution, all stakeholders are connected through one automated workflow and access to the same data. The process is continuously monitored, with alerts of any deviations.
By taking an integrated system approach, manufacturers can realize the benefits of improved operator effectiveness, increased plant availability, reduced maintenance costs and lower lifecycle costs. They can also leverage the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) to improve the safety, efficiency and reliability of operations across a single plant or several plants of an enterprise.
An IIoT infrastructure provides secure methods to capture and aggregate data and apply advanced analytics. Furthermore, it leverages domain expertise and allows end users to use the information to determine methods to reduce or even eliminate manufacturing upsets and inefficiencies. With a large, consolidated set of data provided by experts who understand the unique characteristics of thermal processing applications, manufacturers can apply higher-level analytics for more detailed insight and scale data to meet the varied needs of single-site or enterprise-wide operations.
Putting technology to work
Thermal processing companies can harness the power of connectivity and information sharing to transform their operations. They can use connected devices and integrated systems to capture real-time process information to:
· Improve asset productivity through a better understanding of their equipment
· Identify variability across production processes
· Establish remote monitoring and operational capabilities
· Implement manufacturing best practices
· Enhance safety and regulatory compliance
· Automate repetitive reporting to improve productivity
Industrial heating operations now have access to innovative automation solutions that are focused on turning data into insight – from edge to enterprise – to help improve their bottom line.
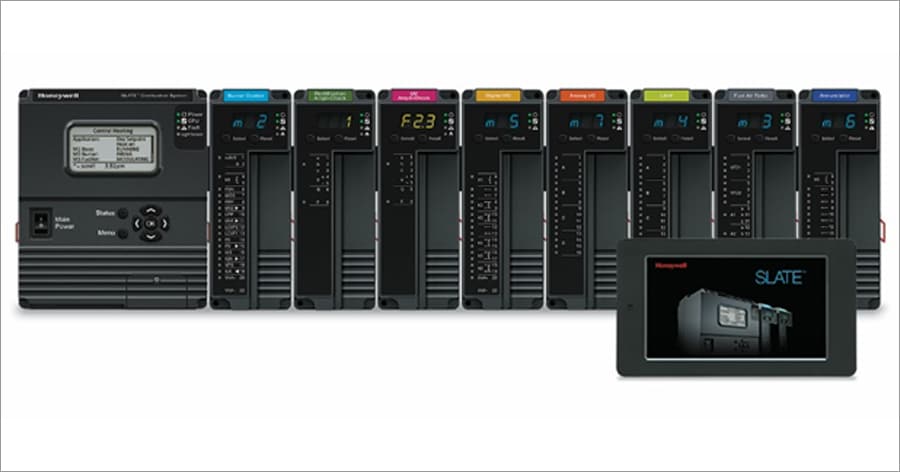

For example, Honeywell’s new SLATE™ Combustion Equipment Manager combines configurable safety features with programmable logic in a single, modular burner control platform. The system reduces the footprint of control room panels and can be easily customized for virtually any combustion application, in less time – and with far less complexity – than traditional solutions. Instead of using separate controllers for different functions, users can simply purchase the modules they need for combustion control and choose how to use them with simple wiring commands. With fewer assets to support and maintain, they can realize lower total cost of ownership.
In conventional control systems, a control panel often contains a programmable logic controller (PLC) combined with separate safety devices such as burner controls. In this case, the safety devices are responsible for the operation and safety of critical equipment. Safety modules operate as discrete, self-contained safety controls.
Previously, data produced by safety devices was connected to whatever the control was doing. If the control function included communication, then the PLC captured and interpreted this information using specialized software. In the latest generation of combustion control systems, all safety module status data and all non-safety control of safety modules are fully integrated into the programmable logic. The base module provides communication and user-programmable logic, while non-safety digital and analog I/O modules provide inputs and outputs for logic. The programmable logic can be used to create any non-safety features required by the equipment that the combustion control system is controlling. This allows an application designer to implement customized, differentiated features in a controller using a configurable touch screen display.
SLATE can also use microprocessor-based burner control platforms, including SIL-3 capable solutions for sequencing multiple burners. Additionally, it can incorporate DIN-mounted universal digital controllers that provide functionality for set point programming, fast scanning and on-board diagnostics. Users can even install intelligent valves designed to communicate with industrial automation systems for enhanced monitoring, reporting and optimization.
Need to make data visible
Most maintenance managers are acquainted with the panic associated with handling critical thermal process failure and investigating potential causes after the incident. In many cases, the issues may require repairs and eventually cause potential unplanned downtime. In order to unleash greater productivity, industrial operations of all sizes are looking for ways to improve the visibility of asset and production issues. Experience has shown that unplanned downtime can result in significant lost revenue. Shutdowns can also lead to substantial response and recovery costs, labor and overhead costs, customer service impact and more.
What factory workers need is an effective way to view and share data before they get to the equipment. This includes mobility tools that enable them to receive real-time alerts when operating parameters exceed limits and track historical data to see when and why issues occurred.
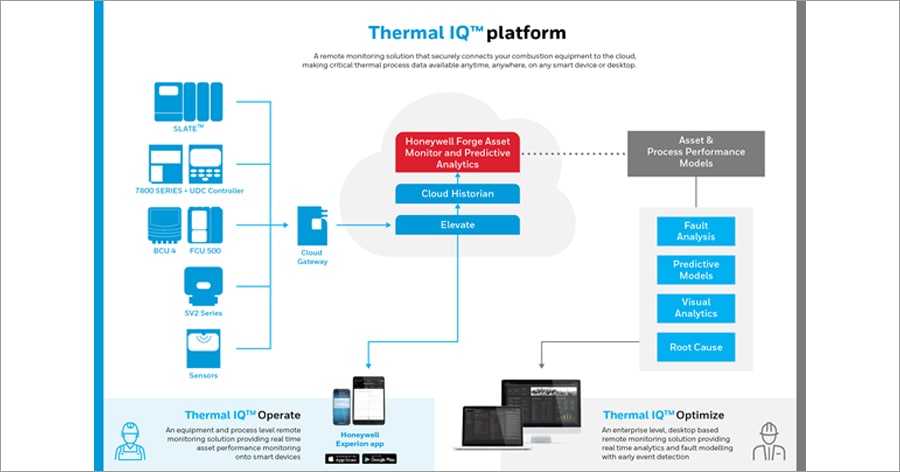
Honeywell’s Thermal IQ™ platform
Honeywell’s response to industry demand for better remote process and equipment monitoring capabilities is Thermal IQ, a platform designed for organizations with limited or no tracking or remote access capabilities and that consequently cannot optimize their thermal process systems.
The solution is also ideal for global organizations with facilities spread across multiple regions that want to bring their operations more tightly together.
Consisting of wireless cellular connectivity, a mobile application and an enterprise-view dashboard, the Thermal IQ platform securely connects combustion equipment to the cloud, making critical thermal process data that is normally confined at the equipment level available anytime, anywhere, on any smart device or desktop.
With Thermal IQ data, users can closely monitor thermal processes without being on site, get real-time alerts when key parameters stray outside normal limits, track historical data over time to identify when and why something happened and provide actionable recommendations. In other words, Thermal IQ turns thermal process data into actionable information.
Built from the ground up with security in mind, the Thermal IQ platform offers a superior level of cyber protection. It uses cybersecurity best practices and the latest security techniques to mitigate threats and further that communication channels are strictly controlled.
Honeywell offers two different solutions based on the Thermal IQ platform: Thermal IQ Operate, an equipment- and process-level remote monitoring solution that provides process operators with real-time asset performance data on smart devices; and Thermal IQ Optimize, an enterprise-level, desktop-based remote monitoring solution that delivers real-time analytics and fault modelling with early event detection.
Platform architecture
Plant combustion equipment management systems and edge devices such as Honeywell Combustion Controls or existing field sensors at equipment, site and regional level capture and communicate key parameters to 4G cellular gateways, which, in turn, transfer data to a secure cloud platform.
Captured field data is then processed in the cloud to generate critical parameters, alarms and trends – revealing insights on thermal processes which can be visualized by users on respective dashboards accessible on mobile devices and desktop computers. Depending on which Thermal IQ platform is being used, deeper, real-time analysis can be extracted, including fault and root cause analysis, predictive analysis and recommendations. Armed with these insights, users can take appropriate, immediate actions to optimize the health of their thermal process equipment.
Thermal IQ™ Operate and its benefits for process operators
Designed for process operators on the move, Thermal IQ Operate is a remote monitoring solution that provides timely, real-time thermal performance information to users via smartphones and devices.
Users get a high-level view of how their equipment is performing and can quickly and easily drill down into individual pieces of equipment to see current alerts and status of key parameters.
They can also compare processes and system performance across the enterprise to identify non-performing assets, which can then be investigated and optimized to bring their performance up to the level of the best-performing assets.
Users can stay ahead of faults or potential failures that can lead to downtime with early alerts. That visibility also enables technicians to arrive at the equipment with the correct tools to repair the problem, while reducing maintenance costs.
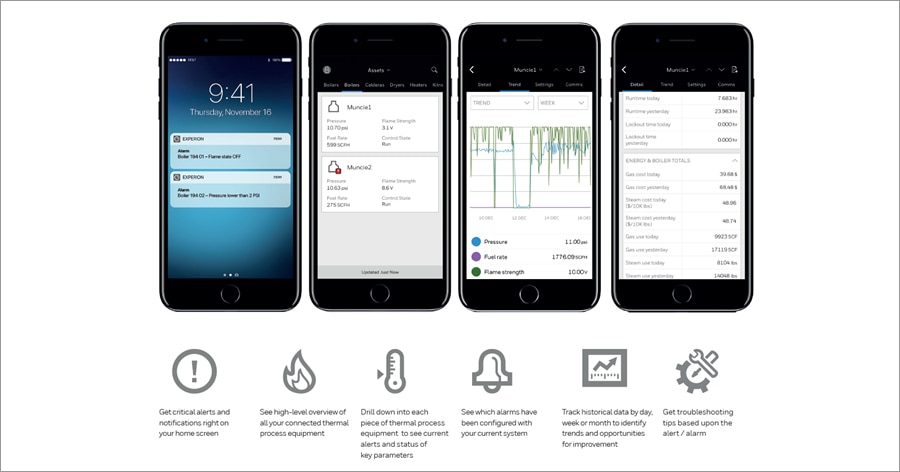
With the capability to track historical data by day, week or month to identify trends and opportunities for improvement, Thermal IQ Operate connects everyone from management to maintenance with insights that drive smarter decisions, such as improving the competency and productivity of people, the efficiency of processes and the performance of assets.
Here is an example to illustrate the power of mobile remote access. A global building material manufacturer deployed Thermal IQ and could identify a performance difference when using a dual flame detector system. This user noted the marginal operation of one flame detector when comparing its performance with the dual system on the same application. The user scheduled maintenance operation on the furnace and a simple cleaning of the flame detector viewing lens returned the system to proper operation while avoiding an unplanned production stoppage.
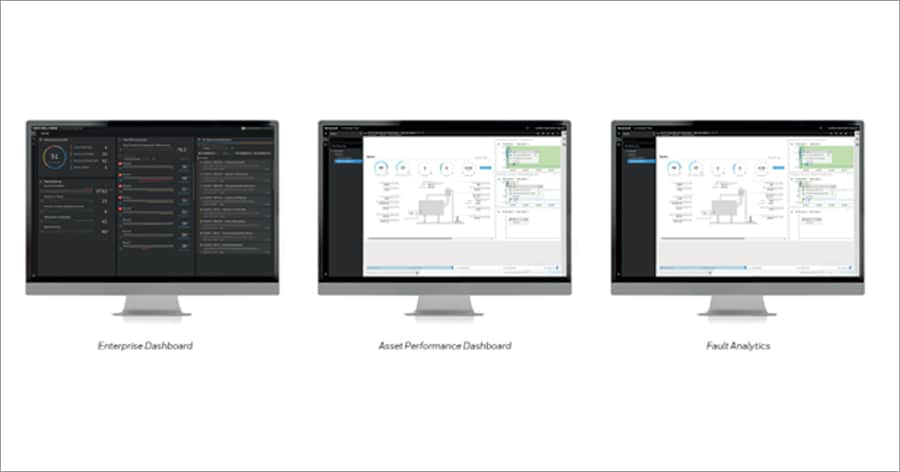
Thermal IQ™ Optimize and its benefits for enterprises
Designed for enterprise desktop use, Thermal IQ Optimize provides real-time analytics and fault modeling with early event detection at plant, equipment and process level to keep thermal equipment running safely, efficiently and effectively.
Based on Honeywell Forge asset and process performance models, the solution extracts data from combustion equipment and thermal processes across the enterprise and delivers a clear, high-level view of thermal process performance via cascading performance dashboards which use the latest visual analytics.
Thermal IQ Optimize processes and measures data in four categories – safety, performance, reliability and efficiency – with the help of inbuilt algorithms that allow users to understand both the health and business cases of their assets at site, division and global level. Users can compare and benchmark equipment data to see which pieces of equipment, sites or regions are performing or failing and then take actions to boost performance levels accordingly.
Using intuitive, interactive fault tree analysis, users can drill into the data of individual assets for an in-depth analysis, enabling them to quickly and easily identify anomalies in equipment functionality or processes, determine their impact on enterprise efficiency and operate before failures occur.
To understand how Thermal IQ Optimize works in practice, let’s quickly examine a case involving a manufacturing site in Muncie, Indiana. There, persistent issues with short-cycling caused additional wear via thermal fatigue stress and excessive valve actuation, as well as reductions in efficiency. Thermal IQ enabled multiple potential causes of the short-cycling to be narrowed to a single root cause. Addressing it not only reduced the short-cycling of the boiler – but also resulted in an efficiency gain of up to 5%.
Conclusion
The latest advances in remote monitoring are freeing personnel from the burden of local equipment monitoring and unleashing facilities’ thermal process potential to drive performance and productivity by connecting people, assets and information across the enterprise.
From the simplest use cases – such as viewing asset data on smartphone or laptop – to more sophisticated applications such as sending real-time notifications when an alarm occurs, connected thermal process solutions are revolutionizing the way process operations run and maintain vital thermal process systems.
Rather than having to integrate, support and maintain purpose-built solutions for combustion control and monitoring, thermal processing operations can now be run more efficiently to optimize production and business results.

